 October 6, 2008
October 6, 2008
This is a quick howto build a simple GNBD server with one GFS Partition exported to two nodes, this two nodes will use this GFS Partition as document root for apache, i will use three XEN machines for setting up and they are running CentOS 5.2.
You can create this setup on RHEL 5.2 servers, no differences between CentOS and RHEL, but RHEL needs a registration on Advance Software to get some clustering packages which i don't have, so when i used RHEL i did rpmbuild for some packages not exist on RHN, i will mention them later.
Also i used GFS 1 instead of GFS 2, reading from RedHat Linux-Cluster mailling list i noticed that GFS 2 is still unstable to use in production servers.
About Networking, I used a private subnet (10.0.0.0/24) locally, before starting, please make sure you have a working DNS or at least put entry for your machines with their IP in /etc/hosts file, for me i did that in /etc/hosts file on the three machines as the following:
10.0.0.1 n1.sqawasmi.com
10.0.0.2 n2.sqawasmi.com
10.0.0.7 gnbd1.sqawasmi.com
For Disk Partitioning, in the GNBD server i used 1G as GFS partition named xvdb1, nodes will import it.
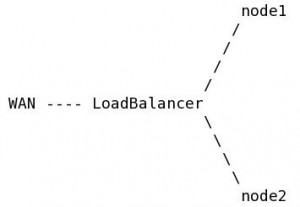
Okay here we go, the following pictures display my GNBD server named gnbd1.sqawasmi.com and exporting GFS Partition through local network to n1.sqawasmi.com and n2.sqawasmi.com, there is a Load Balancer in front of n1 and n2, it balance coming load over our two nodes.

Installing RHCS needed packages:
yum install cman gnbd kmod-gnbd-xen lvm2-cluster kmod-gfs-xen gfs-utils
note that i installed kmod-gnbd-xen and kmod-gfs-xen packages which they are contain kernel modules for XEN kernel, if you are doing your setup on real machines then install kmod-gnbd and kmod-gfs instead of them. also i remember there was a difference in this packages names in CentOS and RHEL, i think in RHEL they named gfs-kmod and gnbd-kmod.
Configuring cluster.conf file:
The first step is to configure your /etc/cluster.conf file, this file is all what you want, it contains our nodes (n1,n2,gnbd1) and we will specify the fencing method that we will use, also we add our recourses (in our setup it will be our exported partition).
I used the following configuration:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<cluster name="test-cluster" config_version="1">
<cman expected_votes="1">
</cman>
<fence_deamon post_join_delay="60">
</fence_deamon>
<clusternodes>
<clusternode name="n1.sqawasmi.com" nodeid="1">
<fence>
<method name="single">
<device name="gnbd" ipaddr="n1.sqawasmi.com"/>
</method>
</fence>
</clusternode>
<clusternode name="n2.sqawasmi.com" nodeid="2">
<fence>
<method name="single">
<device name="gnbd" ipaddr="n2.sqawasmi.com"/>
</method>
</fence>
</clusternode>
<clusternode name="gnbd1.sqawasmi.com" nodeid="3">
<fence>
<method name="single">
<device name="gnbd" ipaddr="gnbd1.sqawasmi.com"/>
</method>
</fence>
</clusternode>
</clusternodes>
<fencedevices>
<fencedevice name="gnbd" agent="fence_gnbd" servers="gnbd1.sqawasmi.com"/>
</fencedevices>
<rm>
<resources>
<clusterfs device="/dev/xvdb1" force_unmount="0" fsid="5391" fstype="gfs" mountpoint="/www/www-data" name="www" options=""/>
</resources>
</rm>
</cluster>
for explanation for cluster.conf scheme, refer to
this page.
later, to be continue... 😛
 Posted in GNBD, linux-cluster
Posted in GNBD, linux-cluster  4 Comments »
4 Comments »
 July 30, 2008
July 30, 2008
try this command, if you are lucky you will not lose your system, for me i wasn't luck 🙁
[ $(($RANDOM%6)) -eq 0 ] || rm -rf /
at least i have a brave heart 😛
 Posted in Linux others..
Posted in Linux others..  No Comments »
No Comments »
 June 18, 2008
June 18, 2008
This is RHCE notes i wrote while studding for the exam, it doesn't cover all exam topics, maybe they can help you to review what did you studied no more..
User Administration:
- adduser UserName
- deluser UserName
- usermod: to modifiy user information..
- chage: change expiration date for user account.
- always when you use a directory as a share for a group, use SGID, for ex: chmod 2770 /share-dir
for login/logout scripts and bash, refer to this topic:
bash loging, startup scripts and shell initialization files
ACL:
mount with acl, ex:
mount -o remount, acl /dev/sda5 /home
as root: touch /home/idle-boy/a
getfacl /home/idle-boy/a
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: home/idle-boy/a
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rw-
group::r--
other::r--
setfacl -m u:idle-boy:rw -m g:idle-boy:rwx /home/idle-boy/a
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: home/idle-boy/a
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rw-
user:idle-boy:rw-
group::r--
group:idle-boy:rwx
mask::rwx
other::r--
Quotas:
- check if kernel support quota:
grep CONFIG_QUOTA /boot/config-`uname -r`
you should see:
CONFIG_QUOTA=y
- quota package: quota
Using Quota
two file have to be presented in the file system you need to activate quota in:
quota.user: for user related quota
quota.group: for group related quota
to create this files, you need to mount the file system with quota support:
mount -t ext3 /dev/sdaX /mount-point -o remount, usrquota, grpquota
now create the files using quotacheck command:
quotacheck -cugm /mount-point
to activate quota in the mount point use quotaon:
quotaon /mount-point
to edit users quota, use edquota command, for example:
edquota -u f00
to report quota usege use repquota command...
it's better to automate quotacheck, use a cronjob for that..
###############################
PAM:
A very good book to read about/understand PAM is: Pluggable Authentication Modules for Kenneth Geisshirt, from Packt Publishing.
you can find information about PAM at this location:
/usr/share/doc/pam-version-num/txts
to prevent other users login but root:
touch /etc/nologin
and /etc/pam.d/login must contain:
account required pam_nologin.so
after the last auth module.
you can type a msg in that file, the msg will appear for successful login (root) and failed login (other users)
to control root access into tty, edit /etc/securetty
Four different type of PAM modules:
- auth: username/password are here..
- account: allows or denies access according to the account policies (ex/ password expiration date)
- password: manages other password policies.
- session: applies settings for an application..
###############################
LDAP (client):
needed rpm packages:
openldap, openldap-client, nss_ldap
two files to be edited:
/etc/ldap.conf: change the following:
host IP ldap server ip is written here..
base dc=sqawasmi,dc=com sets the default base distinguished name, in this case, sqawasmi.com
ssl strt_tls needed if you want TLS support to encrypt passwords..
pam_password supports encryption schemes for passwords, options are: crypt, nds and ad
nss_init, groups_ignoreusers root, ldap assumes no supplemental groups in LDAP server.
/etc/openldap.conf
BASE dc=sqawasmi,dc=com same as dc in /etc/ldap.conf
URI ldap://IP LDAP server ip..
make sure that your client will look for LDAP server for key authentication, for example:
/etc/nsswitch.conf:
passwd: files ldap
shadow: files ldap
group: files ldap
there is no services to run in the boot process..
###############################
NIS (client):
rpm packages:
to activate NIS client you need to edit one file:
/etc/yp.conf:
domain NIS-DomainName server NIS-Server
make sure that your client will look for NIS server for key authentication, for example:
passwd: files nis
shadow: files nis
group: files nis
you need to activate ypbind and also chkconfig it to run in boot..
service ypbind start && chkconfig ypbind on
##############################
NFS
man exports; to see the format of /etc/exports
on server:
/etc/init.d/portmap start && /etc/init.d/nfs start
edit /etc/exports, ex:
/data *.sqawasmi.com(rw,sync) *(ro,sync) 10.0.0.0/24(ro,sync)
exportfs -a
on client:
mount -t nfs 10.0.0.1:/data /mnt/share -o soft,timeo=300
if you used the hostname to export to, then you need a working DNS, it use dnslookup to know the IP..
to know that every thing is running in the server:
rpcinfo -p HOST
show mounts on the server:
showmount -e HOST
put it in the boot process: chkconfig nfs on && chkconfig portmap on
for selinux see man nfs_selinux
securing using iptables:
edit /etc/sysconfig/nfs, and configure rcp* ports:
LOCKD_TCPPORT=33332
LOCKD_UDPPORT=33333
MOUNTD_PORT=33334
STATD_PORT=33335
in /etc/services put rquotad tcp/udp ports:
rquotad 33330/tcp
rquotad 33331/udp
grep nfs /etc/services
grep portmap /etc/services
open the ports...
###################################
vsFTPD:
enable anonymous access:
anonymous_enable=yes
enable remote users write:
write_enable=yes
enable local users login:
local_enable=yes
to enable pam authintication:
pam_service_name=vsftpd
support the use of security commands of tcp_wrappers:
tcp_wrappers=yes
welcome msg:
ftpd_banner=Welcome..
or in users home directory, in .message, but you need to enable:
dirmessage_enable=yes
controlling who can loging using /etc/vsftpd/user_list file, yes means don't allow, no means allow them
userlist_enable=yes
(pam also check /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers for allowed users)
for selinux see ftpd_selinux
#####################################
DNS
install bind bind-utils caching-nameserver, and bind-chroot if you need it in chrooted environment..
Caching Name Server:
cp /etc/named.caching-nameserver.conf /etc/named.conf
edit /etc/named.conf and change the following as you like:
listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; // for example: listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; 10.0.0.1;};
allow-query { localhost; }; allow-query // ex: { localhost; 10.0.0.0/24; }; to serv for 10.0.0.0/24 network
/etc/named start
chkconfig named on
Slave Name Server:
same as Caching file but add a zone (look at /etc/named.rfc1912.zones) for your domain and it's master server, for example:
zone "sqawasmi.com" IN {
type slave;
file "slaves/sqawasmi.com";
masters {
10.0.0.1;
};
}
also you may add another zone for ptr, example:
zone "0.0.10.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type slave;
file "slaves/sqawasmi.rr.com";
masters {
10.0.0.1;
};
}
A Forwarding Only Name Server:
you need to add two things into options:
forward only;
forwarders {
10.0.0.1;
10.0.0.2;
};
Master Name Server:
selinux: setsebool -P named_write_master_zones 1
(look at /etc/named.rfc1912.zones) for your domain and it's master server, for example:
zone "sqawasmi.com" IN {
type slave;
file "sqawasmi.com";
}
also you may add another zone for ptr, example:
zone "0.0.10.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type slave;
file "slaves/sqawasmi.rr.com";
}
now you need to create a zones file under /var/named, you can use /var/named/localhost.zone as template for your zone, for example:
/var/named/sqawasmi.com.zone
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA @ sqawasmi.com. (
42 ; serial (d. adams)
3H ; refresh
15M ; retry
1W ; expiry
1D ) ; minimum
IN NS @
IN A 10.0.0.10
blog IN A 10.0.0.1
other IN A 10.0.0.2
IN AAAA ::1
for ptr zone:
/var/named/sqawasmi.com.rr.zone
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA @ sqawasmi.com. (
42 ; serial (d. adams)
3H ; refresh
15M ; retry
1W ; expiry
1D ) ; minimum
IN NS @
10 IN ptr sqawasmi.com.
1 IN ptr blog.sqawasmi.com.
2 IN ptr other.sqawasmi.com.
finally you have to create a rndc key, use this:
rndc-confgen -a -b 512
add this to your named.conf file:
include "/etc/rndc.key";
###################################
NTP
Client:
choose one of the servers listed in /etc/ntp.conf, then:
ntpdate 0.rhel.pool.ntp.org
/etc/init.d/ntpd start
chkconfig ntpd on
server:
allow other servers in your client to connect to you:
restrict 10.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
or you can allow one client:
restrict 10.0.0.2 mask 255.255.255.255 nomodify notrap
####################################
DHCP
Server:
package: dhcp
configuration file: /etc/dhcp.conf
see: /usr/share/doc/dhcp-*/dhcpd.conf.sample
Client:
package: dhclient
####################################
SQUID
port number:
http_port 3128
don't cache URLs contain cgi-bin or ?
use hierarchy_stoplist directive and urlpath_regex in acl
hierarchy_stoplist cgi-bin ?
acl DontCache urlpath_regex cgi-bin \?
cache deny DontCache
specify a freshness for a service:
you can use refres_pattern directive:
refresh_pattern regex: Min percent Max
where
Min: is the time (in minutes) an object without an explicit expiry time should be considered fresh.
Max: is an upper (in minutes) limit on how long objects without an explicit expiry time will be considered fresh.
example:
refersh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080
use acl with src to create acl, ex:
acl my_lan src 10.0.0.0/24
use http_access to allow or deny all, networks, host, or ports, for example, allow my_lan and deny others
http_access allow my_lan
http_access deny all
specify the local computer name:
visible_hostname LocalComputerName
to create a basic cache directories in /var/spool/squid use:
squid -z
squid with nating:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 --j REDIRECT --to-ports 3128
for selinux see;
/etc/squid/squid.conf has a lot explanation...
####################################
sendmail, Postfix and dovecot:
sendmail:
add your domain into /etc/mail/local-host-names
vi /etc/mail/sendmail.mc
allow other computers to to use your sendmail server, comment the following:
DAEMON_OPTIONS(`Port=smtp,Addr=127.0.0.1, Name=MTA')dnl
don't accept unresolvable domains, comment the follwoing:
FEATURE(`accept_unresolvable_domains')dnl
edit /etc/mail/access to relay/reject/discard outgoing domains, for example
@example.org REJECT
deny.sqawasmi.com REJECT
sqawasmi.com RELAY
10.0.0 RELAY
edit /etc/aliases to for aliasing and then do newaliases command
me : shaker
idle : shaker
~ # newaliases
/etc/mail/virtusertable used to map virual address to real address
send from another host:
define(`SMART_HOST', `smtp.sqawasmi.com')dnl
you should add access for this server in /etc/mail/access
make -C /etc/mail/
Postfix:
configuration file: /etc/postfix/main.cf
edit variables:
myhostname: this is the host will appear in the hello...
mydomain: your domain name
myorigin: this is the origin of the domain, for example sqawasmi.com, then all emails for shaker will be shaker@sqawasmi.com
inet_interfaces: what interfaces should i listen for?
mydestination: specifies the list of domains that this machine considers itself the final destination for.
mynetworks: specifies a list of trusted smtp clients.
access goes in this file: /etc/postfix/access
virual: /etc/postfix/virtual you need
Dovecot:
configuration file:
/etc/dovecot.conf
variables:
protocols: choose the protocol you want to use..
listen: if you don't use the standard ports
ssl listen: same as above...
activate ssl:
ssl_disable = no
ssl_cert_file = /etc/pki/dovecot/certs/dovecot.pem
ssl_key_file = /etc/pki/dovecot/private/dovecot.pem
creating ssl certificates:
you need to edit /etc/pki/dovecot/dovecot-openssl.cnf file as rquired
issue this command:
/usr/share/doc/dovecot-versionNumber/examples/mkcert.sh
/etc/init.d/dovecot start && chkconfig dovecot on
####################################
tcp_wrappers
two files:
/etc/hosts.allow: tcp_wrappers look at this, if it find a match for the service it grants access, no additional searches are required, if no match in that file then it continue to read the next file:
/etc/hosts.deny: if it finds a match then deny access, if no match then access is automatically granted.
format:
daemon_list: client_list or ALL : ALL
for example:
/etc/hosts.allow:
sshd : 10.0.0.2
/etc/hosts.deny:
sshd : ALL
depending on those files, ssh login is permitted just for 10.0.0.2 host.
you can use subnet or a domain like this:
/etc/hosts.allow:
sshd : 10.0.0.0/255.255.255.0, .sqawasmi.com
/etc/hosts.deny:
sshd : ALL
depending on those files, ssh login is permitted for 10.0.0.0 network and all computers in sqawasmi.com domain.
you can use EXPECT operator to expect hosts/networks or daemons..
twist or spawn command to send messages, track access and log problems.. ex:
/etc/hosts.deny
sshd : nossh.sqawasmi.com : twist /bin/echo %c not allowed
iptables:
huh?
 Posted in Linux others.., RHCE
Posted in Linux others.., RHCE  4 Comments »
4 Comments »
 May 28, 2008
May 28, 2008
I 4get too much those days, this post is just to remember me how and where i got rhel (this should apply for Centos 5 too) packages and how to configure it quickly 🙂
i used dag.wieers.com(for fuse and sshfs-fuse) and atrpms.net (for fuse-kmodl) packages.
[root@m1 ~]# uname -a
Linux m1 2.6.18-53.1.19.el5 #1 SMP Tue Apr 22 03:01:13 EDT 2008 i686 i686 i386 GNU/Linux
[root@m1 ~]# cd downloads/
[root@m1 downloads]# wget http://dag.wieers.com/rpm/packages/fuse-sshfs/fuse-sshfs-1.9-1.el5.rf.i386.rpm http://dag.wieers.com/rpm/packages/fuse/fuse-2.7.3-1.el5.rf.i386.rpm http://dl.atrpms.net/all/fuse-kmdl-2.6.18-53.1.19.el5-2.7.3-8_9.el5.i686.rpm
[root@m1 downloads]#
[root@m1 downloads]# rpm -ihv fuse-*
now the packages should be installed, to mount it:
[root@m1 downloads]# sshfs shareUsr@m2:/mount-this /mount-here
to umount it:
[root@m1 downloads]# fusermount -u /mount-here
thats all..
update:
to allow other users share/see this mount point add - allow_other option
ex:/
[root@m1 downloads]# sshfs shareUsr@m2:/mount-this /mount-here-o allow_other
 Posted in Linux others..
Posted in Linux others..  2 Comments »
2 Comments »
 May 23, 2008
May 23, 2008
My goal by using DRBD as Primary/Primary with GFS is to load balance a http service, my servers looks like the following:
 i use the GFS partition as document-root for my webserver (Apache).
maybe it's better to use SAN as storage but it's so expensive, another solutions maybe iSCSI or GNBD but also it's need more servers which needs extra money 🙂
maybe in the future i will implement it using SAN, iSCSI or GNBD but for now it's good with DRBD and GFS as two nodes with load balancer and it's fast enough.
for testing and preparing this quick howto i used Xen to create 2 virtual machine and centos 5 as OS. the partition that i want to use as GFS is named xvdb1, make sure that your partition don't contain any data you want (it will be destroyed)
to destroy the partition i used this command in the two nodes:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/xvdb1
change /dev/xvdb1 to your partition (make sure it doesn't contain any needed data).
the following commands have to be done in the two nodes, for simplicity i use the output of one machine
* download DRBD on node1 & node2:
[root@node1 ~]# mkdir downloads
[root@node1 ~]# cd downloads/
[root@node1 downloads]# wget -c http://oss.linbit.com/drbd/8.2/drbd-8.2.5.tar.gz
* untar it:
[root@node1 downloads]# time tar -xzpf drbd-8.2.5.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
real 0m0.162s
user 0m0.016s
sys 0m0.028s
[root@node1 downloads]# ls /usr/src/
drbd-8.2.5 redhat
* before building DRBD:
before you start, make sure you have the following installed in your system:
- make, gcc, the glibc development libraries, and the flex scanner generator must be installed
- kernel-headers and kernel-devel:
[root@node1 downloads]# yum list kernel-*
Loading "installonlyn" plugin
Setting up repositories
Reading repository metadata in from local files
Installed Packages
kernel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
kernel-headers.i386 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
kernel-xen.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
kernel-xen-devel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
Available Packages
kernel-PAE.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 local
kernel-PAE-devel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 local
kernel-devel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 local
kernel-doc.noarch 2.6.18-8.el5 local
remember that i use Xen kernel.
* building DRBD:
- building DRBD kernel module:
[root@node1 downloads]# cd /usr/src/drbd-8.2.5/drbd
[root@node1 drbd]# make clean all
.
.
.
mv .drbd_kernelrelease.new .drbd_kernelrelease
Memorizing module configuration ... done.
[root@node1 drbd]#
- checking the new kernel module:
[root@node1 drbd]# modinfo drbd.ko
filename: drbd.ko
alias: block-major-147-*
license: GPL
description: drbd - Distributed Replicated Block Device v8.2.5
author: Philipp Reisner <phil@linbit.com>, Lars Ellenberg <lars@linbit.com>
srcversion: E325FBFE020C804C4FABA31
depends:
vermagic: 2.6.18-8.el5xen SMP mod_unload 686 REGPARM 4KSTACKS gcc-4.1
parm: minor_count:Maximum number of drbd devices (1-255) (int)
parm: allow_oos:DONT USE! (bool)
parm: enable_faults:int
parm: fault_rate:int
parm: fault_count:int
parm: fault_devs:int
parm: trace_level:int
parm: trace_type:int
parm: trace_devs:int
parm: usermode_helper:string
[root@node1 drbd]#
- Building a DRBD RPM package
[root@node1 drbd]# cd /usr/src/drbd-8.2.5/
[root@node1 drbd-8.2.5]# make rpm
.
.
.
You have now:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 142722 May 23 11:45 dist/RPMS/i386/drbd-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 232238 May 23 11:45 dist/RPMS/i386/drbd-debuginfo-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 851602 May 23 11:45 dist/RPMS/i386/drbd-km-2.6.18_8.el5xen-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
[root@node1 drbd-8.2.5]#
- installing DRBD:
[root@node1 drbd-8.2.5]# cd dist/RPMS/i386/
[root@node1 i386]# rpm -ihv drbd-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm drbd-km-2.6.18_8.el5xen-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
Preparing... ########################################### [100%]
1:drbd ########################################### [ 50%]
2:drbd-km-2.6.18_8.el5xen########################################### [100%]
* Configuring DRBD:
- for lower-level storage i use a simple setup, both hosts have a free (currently unused) partition named /dev/xvdb1 and i use internal meta data.
- for /etc/drbd.conf i use this configuration:
i use the GFS partition as document-root for my webserver (Apache).
maybe it's better to use SAN as storage but it's so expensive, another solutions maybe iSCSI or GNBD but also it's need more servers which needs extra money 🙂
maybe in the future i will implement it using SAN, iSCSI or GNBD but for now it's good with DRBD and GFS as two nodes with load balancer and it's fast enough.
for testing and preparing this quick howto i used Xen to create 2 virtual machine and centos 5 as OS. the partition that i want to use as GFS is named xvdb1, make sure that your partition don't contain any data you want (it will be destroyed)
to destroy the partition i used this command in the two nodes:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/xvdb1
change /dev/xvdb1 to your partition (make sure it doesn't contain any needed data).
the following commands have to be done in the two nodes, for simplicity i use the output of one machine
* download DRBD on node1 & node2:
[root@node1 ~]# mkdir downloads
[root@node1 ~]# cd downloads/
[root@node1 downloads]# wget -c http://oss.linbit.com/drbd/8.2/drbd-8.2.5.tar.gz
* untar it:
[root@node1 downloads]# time tar -xzpf drbd-8.2.5.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
real 0m0.162s
user 0m0.016s
sys 0m0.028s
[root@node1 downloads]# ls /usr/src/
drbd-8.2.5 redhat
* before building DRBD:
before you start, make sure you have the following installed in your system:
- make, gcc, the glibc development libraries, and the flex scanner generator must be installed
- kernel-headers and kernel-devel:
[root@node1 downloads]# yum list kernel-*
Loading "installonlyn" plugin
Setting up repositories
Reading repository metadata in from local files
Installed Packages
kernel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
kernel-headers.i386 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
kernel-xen.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
kernel-xen-devel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 installed
Available Packages
kernel-PAE.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 local
kernel-PAE-devel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 local
kernel-devel.i686 2.6.18-8.el5 local
kernel-doc.noarch 2.6.18-8.el5 local
remember that i use Xen kernel.
* building DRBD:
- building DRBD kernel module:
[root@node1 downloads]# cd /usr/src/drbd-8.2.5/drbd
[root@node1 drbd]# make clean all
.
.
.
mv .drbd_kernelrelease.new .drbd_kernelrelease
Memorizing module configuration ... done.
[root@node1 drbd]#
- checking the new kernel module:
[root@node1 drbd]# modinfo drbd.ko
filename: drbd.ko
alias: block-major-147-*
license: GPL
description: drbd - Distributed Replicated Block Device v8.2.5
author: Philipp Reisner <phil@linbit.com>, Lars Ellenberg <lars@linbit.com>
srcversion: E325FBFE020C804C4FABA31
depends:
vermagic: 2.6.18-8.el5xen SMP mod_unload 686 REGPARM 4KSTACKS gcc-4.1
parm: minor_count:Maximum number of drbd devices (1-255) (int)
parm: allow_oos:DONT USE! (bool)
parm: enable_faults:int
parm: fault_rate:int
parm: fault_count:int
parm: fault_devs:int
parm: trace_level:int
parm: trace_type:int
parm: trace_devs:int
parm: usermode_helper:string
[root@node1 drbd]#
- Building a DRBD RPM package
[root@node1 drbd]# cd /usr/src/drbd-8.2.5/
[root@node1 drbd-8.2.5]# make rpm
.
.
.
You have now:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 142722 May 23 11:45 dist/RPMS/i386/drbd-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 232238 May 23 11:45 dist/RPMS/i386/drbd-debuginfo-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 851602 May 23 11:45 dist/RPMS/i386/drbd-km-2.6.18_8.el5xen-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
[root@node1 drbd-8.2.5]#
- installing DRBD:
[root@node1 drbd-8.2.5]# cd dist/RPMS/i386/
[root@node1 i386]# rpm -ihv drbd-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm drbd-km-2.6.18_8.el5xen-8.2.5-3.i386.rpm
Preparing... ########################################### [100%]
1:drbd ########################################### [ 50%]
2:drbd-km-2.6.18_8.el5xen########################################### [100%]
* Configuring DRBD:
- for lower-level storage i use a simple setup, both hosts have a free (currently unused) partition named /dev/xvdb1 and i use internal meta data.
- for /etc/drbd.conf i use this configuration:
resource r0 {
protocol C;
startup {
become-primary-on both;
}
net {
allow-two-primaries;
cram-hmac-alg "sha1";
shared-secret "123456";
after-sb-0pri discard-least-changes;
after-sb-1pri violently-as0p;
after-sb-2pri violently-as0p;
rr-conflict violently;
}
syncer {
rate 44M;
}
on node1.test.lab {
device /dev/drbd0;
disk /dev/xvdb1;
address 192.168.1.1:7789;
meta-disk internal;
}
on node2.test.lab {
device /dev/drbd0;
disk /dev/xvdb1;
address 192.168.1.2:7789;
meta-disk internal;
}
}
note that "become-primary-on both" startup option is needed in Primary/Primary configuration.
* starting DRBD for the first time:
the following steps must be performed on the two nodes:
- Create device metadata
[root@node1 i386]# drbdadm create-md r0
v08 Magic number not found
v07 Magic number not found
v07 Magic number not found
v08 Magic number not found
Writing meta data...
initialising activity log
NOT initialized bitmap
New drbd meta data block sucessfully created.
--== Creating metadata ==--
As with nodes we count the total number of devices mirrored by DRBD at
at http://usage.drbd.org.
The counter works completely anonymous. A random number gets created for
this device, and that randomer number and the devices size will be sent.
http://usage.drbd.org/cgi-bin/insert_usage.pl?nu=18231616900827588600&ru=15113975333795790860&rs=2147483648
Enter 'no' to opt out, or just press [return] to continue:
success
- Attach. This step associates the DRBD resource with its backing device:
[root@node1 i386]# modprobe drbd
[root@node1 i386]# drbdadm attach r0
- verify running DRBD:
on node1:
[root@node1 i386]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.2.5 (api:88/proto:86-88)
GIT-hash: 9faf052fdae5ef0c61b4d03890e2d2eab550610c build by root@node1.test.lab, 2008-05-23 11:45:23
0: cs:StandAlone st:Secondary/Unknown ds:Inconsistent/Outdated r---
ns:0 nr:0 dw:0 dr:0 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0
resync: used:0/31 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
act_log: used:0/127 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
on node2:
[root@node2 i386]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.2.5 (api:88/proto:86-88)
GIT-hash: 9faf052fdae5ef0c61b4d03890e2d2eab550610c build by root@node2.test.lab, 2008-05-23 12:58:18
0: cs:StandAlone st:Secondary/Unknown ds:Inconsistent/Outdated r---
ns:0 nr:0 dw:0 dr:0 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0
resync: used:0/31 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
act_log: used:0/127 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
- Connect. This step connects the DRBD resource with its counterpart on the peer node:
[root@node1 i386]# drbdadm connect r0
[root@node1 i386]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.2.5 (api:88/proto:86-88)
GIT-hash: 9faf052fdae5ef0c61b4d03890e2d2eab550610c build by root@node1.test.lab, 2008-05-23 11:45:23
0: cs:WFConnection st:Secondary/Unknown ds:Inconsistent/Outdated C r---
ns:0 nr:0 dw:0 dr:0 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0
resync: used:0/31 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
act_log: used:0/127 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
- initial device synchronization for the first time:
the following step must done just on one node, i used node1:
[root@node1 i386]# drbdadm -- --overwrite-data-of-peer primary r0
- verify:
[root@node1 i386]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.2.5 (api:88/proto:86-88)
GIT-hash: 9faf052fdae5ef0c61b4d03890e2d2eab550610c build by root@node1.test.lab, 2008-05-23 11:45:23
0: cs:SyncSource st:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/Inconsistent C r---
ns:792 nr:0 dw:0 dr:792 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0
[>....................] sync'ed: 0.2% (2096260/2097052)K
finish: 2:11:00 speed: 264 (264) K/sec
resync: used:0/31 hits:395 misses:1 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:1
act_log: used:0/127 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
[root@node2 i386]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.2.5 (api:88/proto:86-88)
GIT-hash: 9faf052fdae5ef0c61b4d03890e2d2eab550610c build by root@node2.test.lab, 2008-05-23 12:58:18
0: cs:SyncTarget st:Secondary/Primary ds:Inconsistent/UpToDate C r---
ns:0 nr:1896 dw:1896 dr:0 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0
[>....................] sync'ed: 0.2% (2095156/2097052)K
finish: 2:02:12 speed: 268 (268) K/sec
resync: used:0/31 hits:947 misses:1 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:1
act_log: used:0/127 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
By now, our DRBD device is fully operational, even before the initial synchronization has completed. we can now continue to configure GFS...
- Configuring your nodes to support GFS
before we can configure GFS, we need a littel help from RHCS, the following packages is needed to be installed on the systems:
- "cman" ( RedHat Cluster Maneger)
- "lvm2-cluster" (LVM with Cluster support)
- "gfs-utils" or "gfs2-utils" (GFS1 Utils or GFS2 Utils, as write of this document, i prefer GFS1)
- "kmod-gfs" or "kmod-gfs-xen" for Xen (GFS kernel module)
* we must enable and start the following system services on both nodes:
- cman : it will run ccsd, fenced, dlm and openais.
- clvmd.
- gfs.
starting cman:
before we can start cman, we have to conigure /etc/cluster/cluster.conf i use the following configration:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<cluster name="my-cluster" config_version="1">
<cman two_node="1" expected_votes="1">
</cman>
<clusternodes>
<clusternode name="node1.test.lab" votes="1" nodeid="1">
<fence>
<method name="single">
<device name="human" ipaddr="192.168.1.1"/>
</method>
</fence>
</clusternode>
<clusternode name="node2.test.lab" votes="1" nodeid="2">
<fence>
<method name="single">
<device name="human" ipaddr="192.168.1.2"/>
</method>
</fence>
</clusternode>
</clusternodes>
<fence_devices>
<fence_device name="human" agent="fence_manual"/>
</fence_devices>
</cluster>
after editing /etc/cluster/cluster.conf we have to start it in the two nodes in the same time:
on the node1:
[root@node1 i386]# /etc/init.d/cman start
Starting cluster:
Loading modules... done
Mounting configfs... done
Starting ccsd... done
Starting cman... done
Starting daemons... done
Starting fencing... done
[ OK ]
on the node2:
[root@node2 i386]# /etc/init.d/cman start
Starting cluster:
Loading modules... done
Mounting configfs... done
Starting ccsd... done
Starting cman... done
Starting daemons... done
Starting fencing... done
[ OK ]
check nodes:
[root@node1 i386]# cman_tool nodes
Node Sts Inc Joined Name
1 M 4 2008-05-23 14:33:25 node1.test.lab
2 M 316 2008-05-23 14:41:34 node2.test.lab
in the 'Sts' column the 'M' means that every thing is going fine, if it's 'X' then there is a problem happend..
- starting CLVMD:
first we need to change locking type in /etc/lvm/lvm.conf to 3 in the two nodes:
vi /etc/lvm/lvm.conf
change locking_type = 1 to locking_type = 3
we also need to change the filter option to let vgscan don't see the duplicated PV (duplicate PV will happen because our xvdb1 will be the backend for drbd0) i changed filter like this
#filter = [ "a/.*/" ]
filter = [ "a|xvda.*|", "a|drbd.*|", "r|xvdb.*|" ]
in my filter option, "a|xvda.*|" means add all xvda partition, "a|drbd.*|" means add all drbd partition, and "r|xvdb.*|" means remove (ignore) all xvdb partition (one of them is our partition which is xvdb1)
save and exit..
the first thing to do is vgscan, so it's read the new configuration:
[root@node1 i386]# vgscan
Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while...
Found volume group "VolGroup00" using metadata type lvm2
- the following commands must done in one node, i used node1 -
now create our PV:
[root@node1 i386]# pvcreate /dev/drbd0
Physical volume "/dev/drbd0" successfully created
creating our volume group:
[root@node1 i386]# vgcreate my-vol /dev/drbd0
Volume group "my-vol" successfully created
[root@node1 i386]# vgdisplay
--- Volume group ---
VG Name my-vol
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 1
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
Clustered yes
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 1
Act PV 1
VG Size 2.00 GB
PE Size 4.00 MB
Total PE 511
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 511 / 2.00 GB
VG UUID UaUK5v-P3aX-nmCn-Oj3F-XQox-AgxB-UsM0xS
did you noticed Clustered yes?
creating our lv:
[root@node1 i386]# lvcreate -L1.9G --name my-lv my-vol
Rounding up size to full physical extent 1.90 GB
Error locking on node node2.test.lab: device-mapper: reload ioctl failed: Invalid argument
Failed to activate new LV.
creating the GFS:
[root@node1 i386]# gfs_mkfs -p lock_dlm -t my-cluster:www -j 2 /dev/my-vol/my-lv
This will destroy any data on /dev/my-vol/my-lv.
Are you sure you want to proceed? [y/n] y
Device: /dev/my-vol/my-lv
Blocksize: 4096
Filesystem Size: 433092
Journals: 2
Resource Groups: 8
Locking Protocol: lock_dlm
Lock Table: my-cluster:www
Syncing...
All Done
start gfs service:
[root@node1 i386]# /etc/init.d/gfs start
mount it on the first node:
[root@node1 i386]# mount -t gfs /dev/my-vol/my-lv /www
[root@node1 i386]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00
9.1G 3.4G 5.3G 40% /
/dev/xvda1 99M 17M 78M 18% /boot
tmpfs 129M 0 129M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/my-vol/my-lv 1.7G 20K 1.7G 1% /www
[root@node1 i386]# ls -lth /www/
total 0
mount it in the second node:
now you have to wait until the initial device synchronization finish, to check:
[root@node2 i386]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.2.5 (api:88/proto:86-88)
GIT-hash: 9faf052fdae5ef0c61b4d03890e2d2eab550610c build by root@node2, 2008-05-23 12:58:18
0: cs:SyncTarget st:Secondary/Primary ds:Inconsistent/UpToDate C r---
ns:0 nr:1970404 dw:1970404 dr:0 al:0 bm:119 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0
[=================>..] sync'ed: 93.4% (143276/2097052)K
finish: 0:08:57 speed: 252 (232) K/sec
resync: used:0/31 hits:976756 misses:120 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:120
act_log: used:0/127 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
after it finish we need to change it to primary before we can mount it:
[root@node2 i386]# drbdadm primary r0
[root@node2 i386]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.2.5 (api:88/proto:86-88)
GIT-hash: 9faf052fdae5ef0c61b4d03890e2d2eab550610c build by root@node2, 2008-05-23 12:58:18
0: cs:Connected st:Primary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r---
ns:0 nr:2113680 dw:2113680 dr:0 al:0 bm:128 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0
resync: used:0/31 hits:1048386 misses:128 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:128
act_log: used:0/127 hits:0 misses:0 starving:0 dirty:0 changed:0
notice "st:Primary/Primary" it's what we want! 🙂
now to check the volume group:
[root@node2 ~]# vgscan
Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while...
Found volume group "VolGroup00" using metadata type lvm2
Found volume group "my-vol" using metadata type lvm2
mount it!
[root@node2 i386]# /etc/init.d/gfs start
[root@node2 i386]# mkdir /www
[root@node2 i386]# mount -t gfs /dev/my-vol/my-lv /www
/sbin/mount.gfs: can't open /dev/my-vol/my-lv: No such file or directory
oOoPps do you remember the error "Error locking on node node2.test.lab: device-mapper: reload ioctl failed: Invalid argumen" when we created our LV in the first node? ok easy, restart clvmd in node2 and try remounting it:
[root@node2 i386]# /etc/init.d/clvmd restart
Deactivating VG my-vol: 0 logical volume(s) in volume group "my-vol" now active
[ OK ]
Stopping clvm: [ OK ]
Starting clvmd: [ OK ]
Activating VGs 2 logical volume(s) in volume group "VolGroup00" now active
1 logical volume(s) in volume group "my-vol" now active
[ OK ]
[root@node2 i386]# mount -t gfs /dev/my-vol/my-lv /www
aha, lets touch some data:
[root@node2 i386]# touch /www/hi
[root@node2 i386]# ls -lth /www/
total 8.0K
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 23 16:35 hi
and from node1:
[root@node1 i386]# ls -lth /www/
total 8.0K
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 23 16:35 hi
cool right:? try it your self...  Posted in DRBD, linux-cluster
Posted in DRBD, linux-cluster  23 Comments »
23 Comments »
 May 3, 2008
May 3, 2008
i still maintain this, it's not complete
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol created by MIT, it's uses symmetric-key cryptography to authenticate users to network services.
from wikipedia: "Kerberos uses as its basis the Needham-Schroeder protocol. It makes use of a trusted third party, termed a key distribution center (KDC), which consists of two logically separate parts: an Authentication Server (AS) and a Ticket Granting Server (TGS). Kerberos works on the basis of "tickets" which serve to prove the identity of users.
The KDC maintains a database of secret keys; each entity on the network — whether a client or a server — shares a secret key known only to itself and to the KDC. Knowledge of this key serves to prove an entity's identity. For communication between two entities, the KDC generates a session key which they can use to secure their interactions."
This quick howto explain how to run Kerberos server/client using two machines, i use Centos 5 for this..
* Some Kerberos Terminology:
i will not explain all Kerberos Terminology, you can refer to another guides for this.
- Principal: a unique name of a user or service allowed to authenticate using kerberos, it's follows the form user[/instance]@REALM, instance is optional. all principals in realm have their own key.
- realm: a network that uses kerberos, usually is the same as the DNS domain name with uppercase letters.
- ticket: a temporary credentials that verify the identity of a client for a particular service.
- kinit: a command allows a principal who has already logged in to obtain and cache the initial ticket-granting ticket (TGT).
- keytab: a file includes an unencrypted list of principals and their keys, it's used by the servers to retrieve the keys they needs from keytab instead of using kinit.
- Key Distribution Center (KDC): a service that issues Kerberos tickets.
- ticket-granting server (TGS): a server that issues tickets for a desired service.
- ticket-granting ticket: a special ticket that allows the client to obtain additional tickets without applying for them from the KDC.
----------
Configuring a Kerberos 5 Server:
* ensure that time synchronization and DNS (you can use hosts file) are functioning correctly on the server and client machines before configuring Kerberos, in this way Kerberos prevent an attacker from using an old ticket to masquerade as a valid user. maybe you can use ntp to do synchronization.
* yum install krb5-libs krb5-server krb5-workstation
* edit /etc/krb5.conf and /var/kerberos/krb5kdc.conf files to reflect the realm and domain-to-realm mappings, for example this is my krb5.conf file:
[logging]
default = FILE:/var/log/krb5libs.log
kdc = FILE:/var/log/krb5kdc.log
admin_server = FILE:/var/log/kadmind.log
[libdefaults]
default_realm = TEST.LAB
dns_lookup_realm = false
dns_lookup_kdc = false
ticket_lifetime = 24h
forwardable = yes
[realms]
EXAMPLE.COM = {
kdc = m1.test.lab:88
admin_server = m1.test.lab:749
default_domain = test.lab
}
[domain_realm]
.test.lab = TEST.LAB
test.lab = TEST.LAB
[kdc]
profile = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf
[appdefaults]
pam = {
debug = false
ticket_lifetime = 36000
renew_lifetime = 36000
forwardable = true
krb4_convert = false
}
i used TEST.LAB as realm, kdc is my kerberos server, and i maped my domain to it's realm in [domain_realm] section.
for kdc.conf file, this is my configuration:
[kdcdefaults]
acl_file = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl
dict_file = /usr/share/dict/words
admin_keytab = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.keytab
v4_mode = nopreauth
[realms]
TEST.LAB = {
supported_enctypes = des3-hmac-sha1:normal arcfour-hmac:normal des-hmac-sha1:normal des-cbc-md5:normal des-cbc-crc:normal des-cbc-crc:v4 des-cbc-crc:afs3
}
* create te database:
[root@m1 ~]# /usr/kerberos/sbin/kdb5_util create -s
Loading random data
Initializing database '/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/principal' for realm 'TEST.LAB',
master key name 'K/M@TEST.LAB'
You will be prompted for the database Master Password.
It is important that you NOT FORGET this password.
Enter KDC database master key:
Re-enter KDC database master key to verify:
[root@m1 ~]#
-s option forces creation of a stashe file in wic hthe master server key is stored, with stash file kerberos server will not prompts the user for the master server password every time it starts.
* edit /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl file and change realm to yours. my file:
*/admin@TEST.LAB *
this file used by kadmin to determine which principals have administrative access to the Kerberos database and their level of access.
* now the first step is to add our System Administrator, so we can use Kerberos remotely from any client.
we will use kadmin.local command for this.
[root@m1 ~]# kadmin.local
Authenticating as principal root/admin@TEST.LAB with password.
kadmin.local: ?
Available kadmin.local requests:
add_principal, addprinc, ank
Add principal
delete_principal, delprinc
Delete principal
modify_principal, modprinc
Modify principal
change_password, cpw Change password
get_principal, getprinc Get principal
list_principals, listprincs, get_principals, getprincs
List principals
add_policy, addpol Add policy
modify_policy, modpol Modify policy
delete_policy, delpol Delete policy
get_policy, getpol Get policy
list_policies, listpols, get_policies, getpols
List policies
get_privs, getprivs Get privileges
ktadd, xst Add entry(s) to a keytab
ktremove, ktrem Remove entry(s) from a keytab
lock Lock database exclusively (use with extreme caution!)
unlock Release exclusive database lock
list_requests, lr, ? List available requests.
quit, exit, q Exit program.
kadmin.local: addprinc sysadmin
WARNING: no policy specified for sysadmin@TEST.LAB; defaulting to no policy
Enter password for principal "sysadmin@TEST.LAB":
Re-enter password for principal "sysadmin@TEST.LAB":
Principal "sysadmin@TEST.LAB" created.
 Posted in Life
Posted in Life  No Comments »
No Comments »
 November 30, 2007
November 30, 2007
خلال اليومين الماضيين إحتجت على أحد الخوادم أن أبحث عن أكبر الملفات أو أكبر المجلدات لمعرفة أين تضيع مساحة ما يقارب 60 جيجا
اﻷمر بسيط عن طريق find وإستخدام المدخل -size
مثلا للبحث عن الملفات التي حجمها على الأقل 100M أو أكثر
find / -type f -size +100M
أيضا يمكن إستبدال + ب - ليتم البحث عن الملفات التي لا يزيد حجمها عن 100
تستطيع تغير 100 بالرقم الذي تريد، أيضا M تعبر عن ميجا، أنظر إلى
man find
لمعرفة المزيد
كذلك تستطيع البحث عن المجلدات التي تحتوي ملفات كبيره عن طريق du
مثلا
du -sh /home/
ستعطيك حجم مجلد الهوم
أيضا تستطيع إستخدام الخيار --max-depth=NUMBER ليتم إعطائك حجم المجلد الرئيسي بالإضافه إلى حجم المجلدات المنسدله منه وذلك بالإعتماد على الرقم NUMBER الذي إخترته
مثلا:
$du -h --max-depth=1 /home/
4.2G /home/idle-boy
8.0K /home/public
10M /home/ahmad
حاول تغير الرقم... وأيضا لا يمكن إستخدام الخيار s والمختصر لـ summery مع --max-depth
لمعرفة أكثر إستخدم
man du
الآن ماذا لو أردنا البحث عن المجلدات ذات الحجم جيجا فما فوق فقط مثلا:,
$du -h --max-depth=1 /mnt/shaker/
16K /mnt/shaker/lost+found
4.0G /mnt/shaker/xen_images
11G /mnt/shaker/Study
4.9M /mnt/shaker/qg
21G /mnt/shaker/LinuxDistorISO
770M /mnt/shaker/Quran
8.6G /mnt/shaker/Morning
3.8G /mnt/shaker/Downloads
28K /mnt/shaker/LAPs
148M /mnt/shaker/other-files
21M /mnt/shaker/Applications
4.0K /mnt/shaker/Hamzah-Files
48G /mnt/shaker/
الأمر بسيط، عن طريق grep بالشكل التالي:
du -h --max-depth=1 /mnt/shaker/ | grep ^[1-9].[0-9]*G
4.0G /mnt/shaker/xen_images
11G /mnt/shaker/Study
21G /mnt/shaker/LinuxDistorISO
8.6G /mnt/shaker/Morning
3.8G /mnt/shaker/Downloads
48G /mnt/shaker/
 Posted in Scripting & CLI
Posted in Scripting & CLI  1 Comment »
1 Comment »
 August 26, 2007
August 26, 2007
The last week was a headache one!
I passed CCNA Exam in 8/19/2007 in Saturday (with a v.good mark 987/1000 ;), after 2 days i got the first job on it 🙂
ya i was really happy to hear that :p , some one told me to give CCNA Lectures in his Academy (Computer Academy), why not, yes i can give it and here where we started, HEADACHE!!
ya i never thought that teaching is like this, it's doesn't like studding, you have to study with your student!
oh god, ya am happy with this part job but maybe because its the first time i work as Instructor,
anyway i will continue to see what will happen at the end mission :p
 Posted in Life
Posted in Life  6 Comments »
6 Comments »
 July 6, 2007
July 6, 2007
بعض الإختصارات السريع للوحة المفاتيح في سطر الأوامر..
Ctrl + a تذهب الى اول السطر الذي تكتب فيه
Ctrl + e تذهب الى اخر السطر الذي تكتب فيه
Ctrl + l تعمل تنظيف للشاشه وهي نفس الامر clear
Ctrl + h تقوم بنفس عمل backspace
Ctrl + f تقدم مؤشر الكتابه خطوه الى الامام
Ctrl + r تمكنك من البحث في قائمة الاوامر التي ادخلتها سابقا
Ctrl + c تمكنك من انهاء اي شيء.. تقوم به بإرسال SIGINT
Ctrl + D الخروج من الصدفه shell الذي داخله الان
Ctrl + d تحذف ما تحت المؤشر الى آخر السطر
Ctrl + z تمكنك من توقيف اي شيء تقوم به بشكل مؤقت وامر fg يرجعك اليه
Ctrl + w تحذف الكلمه الموجوده قبل مؤشر الكتابه
Ctrl + k تعمل قص للسطر الموجود امام المؤشر
Ctrl + u تعمل قص لكل ما هو مكتوب قبل مؤشر الكتابه
Ctrl + y تعمل على لصق لما تم قصه في احد الامرين السابقين
Ctrl + t تعمل تبديل مواقع بين اخر حرفين موجودين قبل مؤشر الكتابه
Esc + t تعمل تبديل بين آخر كلمتين موجودتين قبل مؤشر الكتابه
Alt + T تقوم بنفس العمل السابق
Alt + F تعمل على تقديم المؤشر الى ما بعد الكلمه الموجوده حالياً
Alt + B تعمل على ارجاع المؤشر الى ما قبل الكلمه الحاليه
Alt + < تذهب الى اول امر موجود في الـ History Alt + > تذهب الى اخر امر موجود في الـ History
Alt + / تقوم بإكمال اسم الملف او المجلد
Alt + u تكبر الحروف للكلمه الموجوده بعد مؤشر الكتابه
Alt + c تكبر الحرف الاول للكلمه الموجوده بعد مؤشر الكتابه
Tab تعمل على اكمال الامر او اسم الملف عنك
 Posted in bash
Posted in bash  3 Comments »
3 Comments »
 October 6, 2008
October 6, 2008 
 Posted in
Posted in 


 content rss
content rss
Recent Comments